China GDP changes 1949-2022

China GDP changes 1949-2022
China has come a long way since the establishment of the People’s Republic of China in 1949. One of the most significant changes during this time has been the country’s economic development, with the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) experiencing remarkable growth over the years. Let’s take a closer look at the Chinese GDP changes from 1949.
After the establishment of the People’s Republic of China in 1949, the country faced numerous challenges, including a lack of resources, infrastructure, and investment. The government’s primary focus was on restructuring the economy, which resulted in a significant decline in GDP in the early years. In the early 1950s, the Chinese economy grew at an average annual rate of 4.4%, but this figure decreased to 2.9% in the late 1950s due to the Great Leap Forward campaign.
The Cultural Revolution, which lasted from 1966 to 1976, had a significant impact on China’s GDP, with the annual growth rate dropping to 0.6% during this period. However, after the end of the Cultural Revolution, the Chinese economy started to recover, and by the end of the 1970s, the annual growth rate had increased to 6.4%.
In the 1980s, China adopted a series of economic reforms, which led to a period of rapid economic growth. The annual growth rate averaged around 9.5% from 1979 to 2010. During this time, China transformed from an agrarian economy to a global manufacturing powerhouse, becoming the world’s second-largest economy in 2010. This period of sustained economic growth was driven by a combination of factors, including foreign investment, increased trade, and the adoption of market-oriented economic policies.
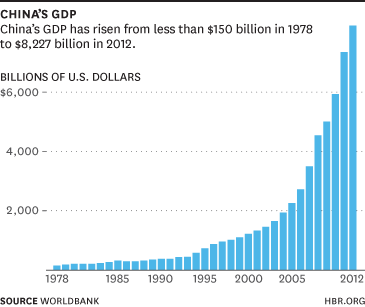
China’s economic growth slowed down slightly in the 2010s, with the annual growth rate averaging around 6.7% from 2011 to 2020. Despite this, China has continued to make significant progress, becoming a leader in several industries, including technology and renewable energy.
In recent years, the Chinese government has placed a greater emphasis on sustainable economic growth and has implemented policies aimed at reducing inequality and addressing environmental concerns. The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on the Chinese economy, with the country experiencing its first economic contraction in decades in the first quarter of 2020. However, China’s GDP rebounded quickly, growing by 2.3% in 2020, making it one of the only major economies to experience positive growth during the pandemic.
In conclusion, China’s economic development since 1949 has been a remarkable journey. From a struggling agrarian economy to a global manufacturing powerhouse, the country’s GDP growth has been driven by a combination of factors, including foreign investment, increased trade, and market-oriented economic policies. Despite some challenges, China has continued to make significant progress, becoming a leader in several industries and placing a greater emphasis on sustainable economic growth.








